The Future of Industrial Automation: Global Trends and India's Emerging Role
The relentless march of technology continues to redefine industries across the globe, and at the forefront of this transformation lies industrial automation.
Poised for substantial expansion, the global Industrial Automation market is projected to surge at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.8%, propelled by the dynamic forces within the Americas and, most notably, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region. This analysis delves into the multifaceted landscape of industrial automation companies, with a particular focus on the burgeoning opportunities and unique characteristics of the Indian market.
The Global Industrial Automation Landscape: A Regional Perspective
The Global Industrial Automation market is a complex tapestry woven from the distinct threads of regional economic conditions, digital transformation, technological adoption rates, and strategic government initiatives. While the Americas and Europe hold significant positions, it is the APAC region that is emerging as the primary engine of growth.
APAC’s ascent in the industrial automation arena is fueled by a potent combination of factors, most prominently the rapid pace of industrialization and the burgeoning manufacturing sectors within countries like China, India, and South Korea. These nations have embraced the principles of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, injecting substantial investments into the development and deployment of cutting-edge automation technologies. This proactive approach is not merely about increasing production output; it signifies a fundamental shift towards creating more efficient, resilient, and globally competitive manufacturing ecosystems.
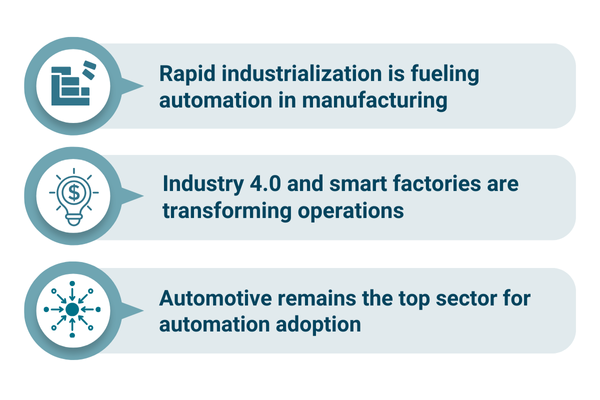
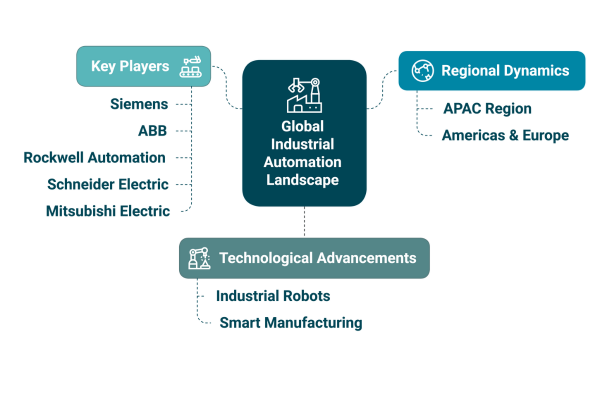
Within the broader spectrum of industrial automation, certain components are experiencing particularly robust growth. Industrial robots stand out as the frontrunners, with projections indicating a remarkable CAGR of 12%. This surge in demand for robotic process automation underscores the increasing need for precision, repeatability, and adaptability in automating manufacturing processes. From intricate assembly tasks to hazardous materials handling, different types of industrial robots are proving to be indispensable assets in a wide range of industries.
The Automotive sector is anticipated to remain the largest end-use industry for industrial automation solutions, driven by the ever-increasing demand for robotics, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. These technologies play a critical role in optimizing assembly lines, enhancing welding processes, and ensuring the overall efficiency of automotive manufacturing operations. As the Automotive industry continues to evolve with the rise of electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies, the demand for advanced automation solutions is only expected to intensify.
Key players such as Siemens, ABB, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, and Mitsubishi Electric are at the helm of this technological revolution, driving innovation and shaping the future of industrial automation on a global scale. Their comprehensive portfolios, extensive expertise, and strategic partnerships are instrumental in facilitating the adoption of automation technologies across various industries.
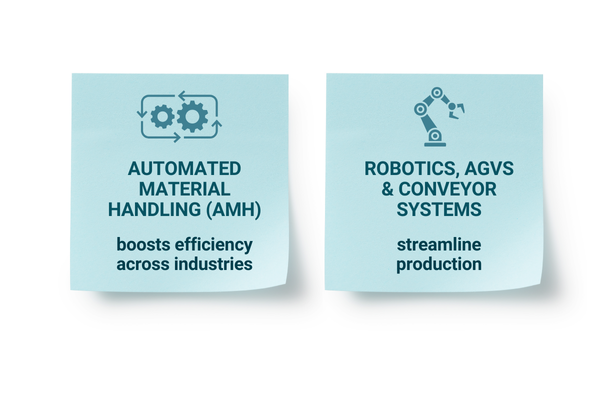
Applications of Industrial Automation
The transformative power of industrial automation is evident in its diverse applications, ranging from automated material handling to comprehensive factory optimization. These applications are not limited to a single industry; rather, they are adaptable and scalable across a wide range of sectors, each benefiting from the unique advantages that automation provides.
1. Automated Material Handling (AMH):
AMH systems are revolutionizing the way materials are moved, stored, and managed within industrial facilities. By automating these processes, and process control, companies can significantly reduce labor costs, improve efficiency, and minimize the risk of errors or damage to goods. AMH solutions encompass a wide range of technologies, including:
-
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Self-guided vehicles that navigate through facilities using pre-defined paths or sensors, transporting materials without human intervention
-
Robotic Palletizing and Sortation Systems: Robotic systems that automate the stacking and sorting of materials onto pallets, increasing throughput and reducing the physical strain on human workers
-
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Software that provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, optimizes storage locations, and streamlines order fulfillment processes
-
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): Automated machinery to store and retrieve materials from high-density storage racks, maximizing space utilization and improving inventory control
-
Conveyor Systems: Conveyor belts that provide a continuous flow of materials between different workstations or storage areas, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall efficiency
The benefits of AMH are particularly pronounced in industries with complex supply chains, high volumes of materials, or stringent quality control requirements. Examples include:
-
Pharmaceuticals: AGVs are used to transport active pharmaceutical ingredients in cleanrooms, ensuring the integrity and purity of these sensitive materials. Automated inventory management systems track temperature-sensitive products, preventing spoilage and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements
-
Automotive: AGVs move car chassis and heavy components across assembly lines, streamlining the manufacturing process. Robotic palletizing systems handle spare parts and finished vehicles, optimizing logistics and reducing labor costs
-
Food & Beverage: Conveyor belts move packaged foods seamlessly through production lines, while robotic arms sort and load finished goods with speed and precision. Cold storage automation systems manage perishable items, ensuring freshness and minimizing waste
-
Oil & Gas: AGVs are used for transporting drilling equipment and materials in offshore platforms. The sector also uses automated pipeline storage management and palletizers or sortation systems for sorting and packaging of oil derivatives
-
Power: Robotics are used to manage storage of electrical components like transformers, real-time inventory tracking using RFID systems tracks spare parts and automated material handling is used to transport heavy equipment in power plants
2. Factory Automation
Factory Automation encompasses a broader range of technologies that automate various aspects of the manufacturing process, from production planning and control to quality assurance and maintenance.
By integrating these technologies, companies can create smart factories that are more efficient, flexible, and responsive to changing market demands.
Key components of factory automation include:
-
SCADA Systems: Collect and analyze data from sensors and other devices, providing real-time insights into production metrics, energy consumption, and other key performance indicators
-
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Automate repetitive tasks, such as mixing, packaging, and sorting, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of human error
-
Distributed Control Systems (DCS): Provide centralized control and monitoring of complex industrial processes, ensuring optimal performance and preventing equipment failures
-
Robotic Systems: Often connected by industrial automation protocols and used in smart manufacturing. Functions often include welding, painting, assembly, disassembly, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing
-
Sensors: Monitor various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate, providing valuable data for process control and optimization
-
Actuators: Control the movement of valves, pumps, and other mechanical devices, enabling precise control of industrial processes
-
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): Optimize the manufacturing process by monitoring, tracking, documenting, and controlling the entire production lifecycle
The benefits of factory automation are evident across a wide range of industries:
-
Pharmaceuticals: DCS systems ensure precise control of drug formulation processes, while SCADA systems monitor cleanroom conditions to maintain product quality
-
Automotive: Robotic systems perform welding, painting, and assembly tasks with speed and precision, while SCADA systems monitor vehicle production metrics in real-time
-
Food & Beverage: PLCs automate mixing and packaging processes, while sensors monitor temperature and pressure to ensure food safety and quality
-
Oil & Gas: Sensors are used for pipeline flow and leak detection, robotic systems for inspection of pipelines and offshore rigs, while DCS are used to manage chemical processes in petrochemical plants and PLCs for pipeline automation and control
-
Power: Sensors are used for monitoring voltage, current, and temperature in smart grids and robotic systems for inspection & maintenance of substations. MES are used for managing energy production schedules and Actuators for controlling circuit breakers and transformers

Industrial Automation Solutions Mix
Industrial automation solutions are not one-size-fits-all. Rather, they can be broadly categorized into off-the-shelf scalable solutions and highly customized solutions, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
-
Off-the-Shelf Scalable Solutions:
These are pre-designed solutions developed for general use across a broad range of industries and applications. They are ready to deploy with minimal setup or adjustments, offering faster implementation and lower upfront costs. Scalable solutions can grow with a business, allowing companies to add more units or expand the system as their needs increase.
Examples of off-the-shelf scalable solutions include:
-
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) for moving goods in standardized pallets within a warehouse
-
Pick-to-light & put-to-light systems that use mobile barcode scanners and digital light displays to guide warehouse pickers
-
Autonomous mobile robots that use GPS systems to create effective routes through a specific warehouse
Highly Customized Solutions:
These are tailor-made solutions built from scratch or heavily modified to meet the very specific requirements of a business or industry.
Unlike off-the-shelf options, these are not ready to use out of the box and require extensive design, engineering, or coding.
Examples of highly customized solutions include:
-
Robotic arms in car assembly designed specifically for tasks like welding, painting, or assembling unique components
-
Customized robotic surgery systems tailored to perform high-precision tasks like heart surgery or urology
-
Predictive analytics software designed for major retailers to optimize restocking based on customer behavior and weather patterns
The choice between off-the-shelf and highly customized solutions depends on the specific needs and priorities of the company. Off-the-shelf solutions offer faster implementation and lower costs, while highly customized solutions provide greater flexibility and integration with existing systems.
The Indian Automation Market
While the global trends provide a broad overview, a closer examination of the Indian Automation Market reveals a landscape brimming with untapped potential. Currently estimated at USD 13.2 billion in 2023, the Indian market is poised for exponential growth, with projections indicating a CAGR of 14.3%. This rapid expansion is fueled by a confluence of factors, including the growing adoption of automation technologies across manufacturers in India as well as the Automotive, and IT sectors.
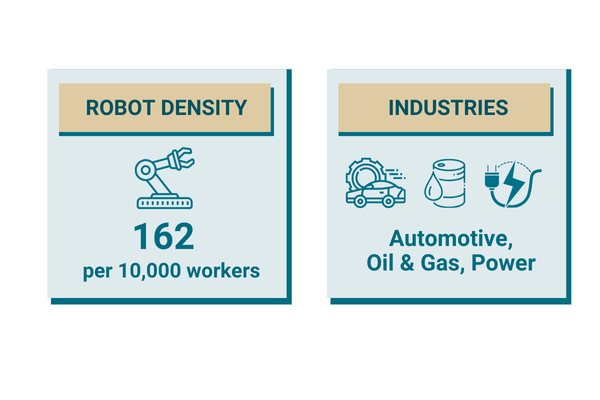
The Power, Oil & Gas, and Automotive Industries are currently at the forefront of automation adoption in India, recognizing the immense potential for improving operational efficiency, enhancing safety, and reducing costs through the implementation of advanced automation solutions.
However, the true potential of the Indian market lies in its relatively low robot density compared to other industrialized nations. With only 162 robots per 10,000 manufacturing workers, India lags significantly behind China, which boasts a robot density of 392. This disparity highlights the vast opportunities that exist for increasing the adoption of robotics in Indian manufacturing, particularly as companies seek to enhance productivity, improve quality, and compete effectively in the global marketplace.
Leading Indian players such as Wipro Pari, Titan Automation Solutions, and Larsen & Toubro are actively contributing to the growth of the domestic automation market, while global players are also making significant inroads, bringing their expertise and advanced technologies to the Indian landscape. This interplay of local and international players is fostering a dynamic and competitive environment, driving innovation and accelerating the adoption of scalable solutions for industrial automation.
Growth Drivers in the Indian Market: A Unique Set of Opportunities
The Indian market for Industrial Automation is driven by a unique set of factors that are creating a fertile ground for growth and innovation.

-
Industry 4.0 and Digital Transformation: The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles is enabling smart manufacturing with real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized operations. The integration of technologies such as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (ML) is enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making.
-
Global Supply Chain Dynamics: The shift in global supply chain dynamics, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, has highlighted the need for resilience and agility.
Many companies are re-evaluating their manufacturing strategies and considering automation to mitigate risks and disruptions.
-
Growth of Key Industries: India’s position as a major automotive hub drives automation adoption in assembly lines and supply chain management. The "Make in India" initiative has spurred investments in electronics production, increasing demand for automation. Rising demand for packaged goods and compliance with hygiene standards is driving automation in food and beverage manufacturing
-
Increasing Labor Costs and Safety Requirements: With rising labor costs, especially in manufacturing, there's a growing incentive for industries to adopt automation to reduce dependency on manual labor and improve operational efficiency. Automation ensures compliance with workplace safety standards and reduces accidents in hazardous environments
Embracing the Future of Industrial Automation
The global Industrial Automation Market is poised for significant growth, driven by technological advancements, changing economic conditions, and a growing recognition of the benefits that automation can provide. While the APAC region is leading the charge, the Indian market presents a particularly compelling opportunity for investors and industry participants.
By understanding the key market drivers, regional dynamics, and technological trends, companies can position themselves to capitalize on the transformative power of industrial automation and shape the future of manufacturing. The journey towards greater efficiency, productivity, and resilience is paved with automation, and those who embrace this reality will be best positioned for success in the years to come.

